In the age of renewable energy, hydrogen is emerging as a clean, versatile fuel source with the potential to revolutionize how we power our lives. This lightweight element, known for being the most abundant substance in the universe, is produced through various technologies that allow us to harness its energy. But how exactly is hydrogen manufactured today, and what are its most popular uses in our modern world? Let’s explore.
How Hydrogen Is Manufactured
Hydrogen is not found in its pure form on Earth, so it must be extracted from other substances. The production methods for hydrogen vary, with the most common processes being:
1. Steam Methane Reforming (SMR)
Steam Methane Reforming is the most widely used method for hydrogen production. In this process, natural gas (mainly methane) reacts with steam at high temperatures to produce hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide. While efficient and cost-effective, SMR generates significant carbon emissions, raising concerns about its environmental impact.
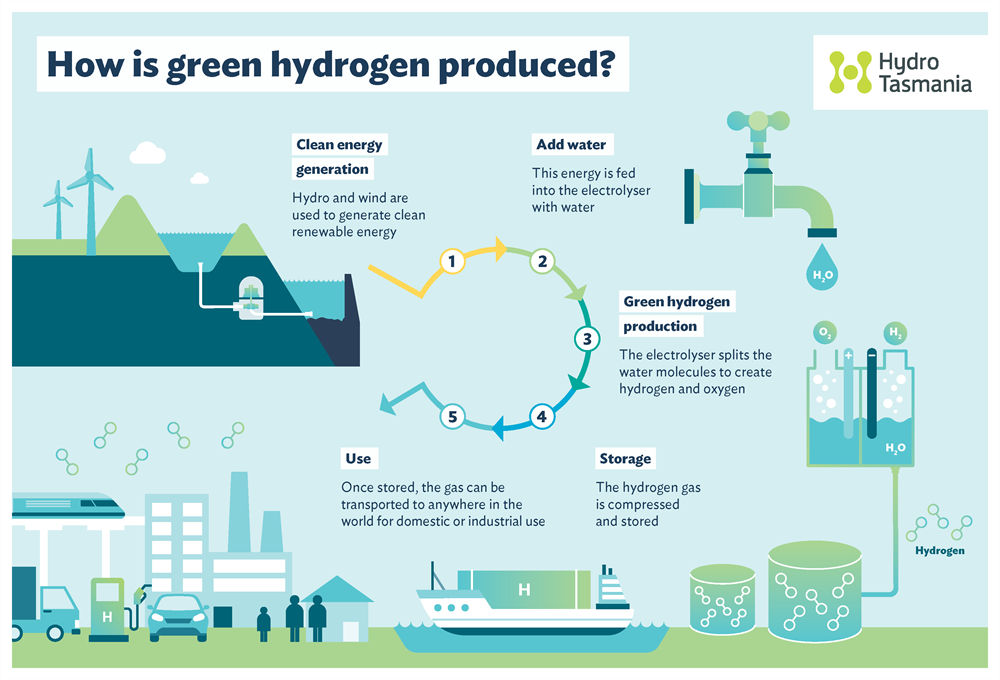
2. Electrolysis of Water
Electrolysis is a cleaner method of hydrogen production, especially when powered by renewable energy sources such as solar or wind. It involves passing an electric current through water (H₂O), splitting it into hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂). The use of renewable energy in electrolysis allows for the production of “green hydrogen,” a sustainable and zero-emissions alternative to fossil-fuel-derived hydrogen.
3. Biomass Gasification
In this method, organic materials (biomass) are heated in a controlled environment to produce a mixture of gases, including hydrogen. While not as common as SMR or electrolysis, biomass gasification is gaining traction due to its potential to utilize waste materials and reduce overall emissions.
4. Partial Oxidation
Partial oxidation involves reacting hydrocarbons like natural gas or coal with oxygen at high temperatures to produce hydrogen. While it is efficient, this process also generates carbon emissions, making it less environmentally friendly than some alternatives.
The Most Popular Applications of Hydrogen Today
As hydrogen production technology evolves, its applications are expanding across various sectors, contributing to cleaner energy solutions and innovative industrial processes. Below are some of the most prominent uses of hydrogen today:
1. Energy Storage and Power Generation
Hydrogen is playing a key role in energy storage systems. Renewable energy sources, like solar and wind, are intermittent by nature. Hydrogen offers a solution to this challenge by storing excess energy in the form of hydrogen gas. This stored hydrogen can later be used in fuel cells to generate electricity, providing a stable and reliable energy source, even when the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing.

2. Fuel Cells for Transportation
One of the most exciting applications of hydrogen is in fuel cells, particularly for transportation. Fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) use hydrogen to generate electricity, powering electric motors without the need for heavy batteries. Unlike conventional vehicles, FCVs emit only water vapor, making them an attractive alternative to fossil fuel-powered cars. Companies like Toyota, Hyundai, and Honda are already rolling out hydrogen-powered vehicles, and many believe hydrogen fuel could play a significant role in the future of transportation.

3. Industrial Uses
Hydrogen is a key component in many industrial processes. In the chemical industry, it is essential for producing ammonia, a critical ingredient in fertilizers. Hydrogen is also used in oil refining, where it helps convert crude oil into gasoline and other fuels. Additionally, hydrogen plays a role in metal production and processing, where it is used to remove impurities and improve the quality of metals like steel.
4. Hydrogen for Heating and Cooling
Hydrogen is increasingly being used as a clean fuel for heating and cooling systems. When combusted, hydrogen produces heat without emitting carbon dioxide, making it a viable option for reducing greenhouse gas emissions in residential and commercial buildings. Some countries are even exploring hydrogen as a replacement for natural gas in domestic heating systems.

5. Aviation and Space Exploration
Hydrogen has been used for decades in space exploration. It powers rockets, including the main engines of NASA’s Space Shuttle, by burning liquid hydrogen with liquid oxygen. As the world looks toward the future of air travel, hydrogen-powered aviation is being explored as a way to decarbonize long-haul flights. Aircraft manufacturers are investigating hydrogen fuel cells and combustion engines as alternatives to traditional jet fuel.
The Road Ahead for Hydrogen
While hydrogen holds great promise as a clean energy carrier, challenges remain. The cost of hydrogen production, especially through green methods like electrolysis, is still high compared to traditional fossil fuels. Infrastructure for hydrogen distribution and storage is also limited, which hinders its widespread adoption.
However, with ongoing advancements in hydrogen production technology and growing investments in hydrogen infrastructure, the future of hydrogen looks bright. As we strive toward a more sustainable world, hydrogen could play a pivotal role in decarbonizing industries, transforming transportation, and supporting renewable energy systems.
Conclusion
Hydrogen’s versatility and potential as a clean energy solution are driving its growing importance in today’s world. Whether it’s powering vehicles, fueling industrial processes, or enabling renewable energy storage, hydrogen is becoming a key player in the global transition toward a sustainable energy future. As we continue to innovate in its production and application, hydrogen could be the fuel that powers the next generation of technologies and industries.
To discuss and cooperate in developing this technology, please contact us
BIG NANO TECHNOLOGY
Hotline: (+84) 879 808 080 – (+84) 868 939 595
Email: sales@bignanotech.com








